Understanding AI and its Role in the Contact Centre (CCaaS) and the future of Customer Experience (CX)
The customer experience industry has always been at the forefront of new technology usage. Customers demand the highest level of quality and will purchase from the brands that provide it. Customers also bring complex problems that can now be resolved by new technology that was previously not capable. Both of these facts mean that being able to differentiate with high-quality customer service is vital for brands competing in the modern digital ecosystem.
This article will lay out the interactions between AI, the contact centre and the future of AI in CCaaS and CX deployments. It will start by explaining Cavell’s definition and understanding of AI to make sure we all share the same lexicon and then move on to the industry specific topics.
As a bit of fun, I asked an AI programme to make an image of a robot built from telecoms equipment. I don’t think it succeeded. Is that a car radio? This sort of illustrates the point that while AI is coming along, it isn’t yet the multi-purpose all powerful tool people would believed.
What is AI?
What exactly does AI Mean?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a piece of software that is capable of self-directed learning and growth.
Everyone acknowledges that there does not exist a fully self-aware and independent AI, as has been idealised in science fiction movies.
People working in the market focus on specific expressions of Artificial Intelligence, which can be seen as use cases or as a progression-based model.
The four types of AI are: Reactive Machines; Theory of Mind; Limited Memory; and Self-Aware. There is also the concept of Machine Learning, which is a component of AI that some people use as a separate solution.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning is the concept of creating a programme that can improve its function over time by repeating the same task.
It is used in AI as a component, but AI takes the concept and builds more systems on top of it.
In practice, this involves the creation of a piece of software capable of performing a series of tasks and giving it criteria for a successful completion of the task, along with a dataset to use to attempt to complete said task. E.g., Giving a programme the task of solving a Rubix cube, and the knowledge of colours and potential turns, and then letting the machine determine the optimal actions to achieve the goal (a solved cube).
What are the 4 types of AI?
The four types of AI are: Reactive Machines; Limited Memory; Theory of Mind; and Self-Aware.
Reactive Machines – are machines designed to respond in a similar way to identical situations. These situations can be complex and varied but there is no capability or possibility for the response to change.
In a contact centre, a reactive machine virtual agent will allow inbound callers to select button 1, and always route everyone who selects 1 to a programme that lets them cancel their contract.
Limited Memory – builds on the reactive process by allowing the machine to change its responses over time. It does this by using historical and observational data of its own actions and situation combined with additional data provided by the programmers to learn how to improve actions based on its available memory.
In a contact centre, a limited memory AI will be able to evaluate the differences between callers and would notice over time that a certain profile of caller was likely to hang up if directed towards an automated machine and would choose to direct them to a human agent instead.
Theory of Mind – is the creation of the capability for AI to understand, process and react based on emotions. This is a complex process as humans express many emotions in many ways, and the expression of emotion is highly individual.
In a contact centre, a Theory of Mind AI, would be able to question an inbound caller and detect the emotions that caller was presenting and respond accordingly. Does the person sound frustrated or worried? Then they should speak to a human agent. Do they sound calm and are they asking to do a simple admin task? Then direct them towards the automated process.
Self-Aware – A Self-Aware AI will have its own emotions, awareness, and desires. These will be pre-programmed, and the AI will operate with an awareness of the interaction of its own emotions and desires with those of people it meets.
In the contact centre, a self-aware AI can provide a sympathetic emotional response. It will likely desire to provide a successful customer service as that will make it happy and make its customers happy. This means that if it cannot complete its task due to policies and restrictions, it will be able to provide a sympathetic sadness response as both the AI and the customer are frustrated that it cannot complete the task.
How is AI used in business?
The primary uses of AI in business are the automation of labour-intensive tasks, the provision of assistance with creativity and the management of data and knowledge.
Automated Cognitive Work
The most common use of AI is the automation of repetitive tasks that require a low-level of cognitive analysis. Across many fields, there are many tasks that can be solved by the application of the same principles every time. AI is being used to analyse those tasks, determine what principles need to be applied, and attempting to resolve the task with that approach. If this approach fails, it will flag the issue to be resolved by a human engineer.
An example for this is summarising reports. An AI can use language recognition to identify the most relevant points and pieces of data in a report and can then summarise that report for a human reader. It could then draft an email based on that summary to be shared with colleagues.
Assistance with Creativity
AI can be used to help with creative enterprises like writing/visualisation. It achieves this task by understanding similar tasks and providing recommendations based on how the same problem has been solved in other cases.
In practice this can be as simple as suggesting sentences and grammatical changes, or proposing a diagram or graph based on what has been written. However, it can go as far as to provide AI-generated articles and images based on inputted criteria e.g. ChatGPT.
What is an example of a business AI?
A business AI is any AI that is used to enhance the operations within a business setting.
Some examples of business use cases for AI are creative assistance, optimisation and trend tracking, routine automation, and personalised learning and training.
Is Artificial Intelligence the future of work and business?
Yes, artificial Intelligence is the future of work and business. The power of AI promises to impact every part of doing business in the future. AI will not only change how we work, but also the work that we do.
What will AI be used for in the future?
In the future AI will mainly be used for the automation of repetitive tasks. This could include admin, reviewing documents, summarisation of complex documents and organisational tasks.
All business operations will be impacted by AI. AI will be used to improve and streamline every business process. It will also create new jobs, opportunities and methodologies within businesses.
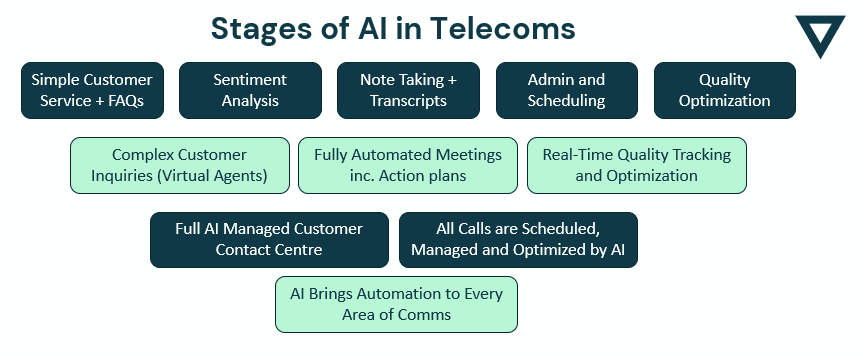
AI in Telecoms
How will AI impact Telecoms?
The main impact that AI will have on telecoms is to automate calling for consumers and to automate customer service by companies. Consumers will use AI to make admin calls and save themselves time. Companies will use AI to provide more personalised customer service interactions.
Some examples of this interaction can be seen in the July 2023 announcement about the deployment of Microsoft Copilot in Teams Phone. This adds the ability to get real-time summarisation and insight, as well as live note taking and action lists.
AI will also be used for telecom operations automation and optimisation. Telecoms networks require large amounts of management, control, and maintenance. AI will provide automated diagnosis, detection and resolution of issues with the telecoms network.
Can AI make phone calls?
Yes, AI can make phone calls. This is currently not that sophisticated, but the technology is being developed to allow AI to make more elaborate phone calls on your behalf. Google made a demo of this technology in 2018, but it has not yet become commonplace. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JvbHu_bVa_g
This has initially taken the form of calling someone on your behalf with a dictated message. However, the technology is being developed to enable AI assistants to have conversations with people for you. For example, if an AI assistant is asked to schedule a haircut, it will know the usual hairdresser you use and then call that hairdresser, ask for an appointment, and book it into a free spot in your diary.
What is AI calling?
AI calling is when an AI makes phone calls on behalf of, or instead of, a human being.
This could be automated interactive calls for sales or customer service reasons. It could also be scheduling, management and admin calls as part of a virtual assistant role.
Can AI replicate voices?
Yes, AI can replicate voices based on a sampling of audio. AI can also turn scripts of written language into speech audio recordings with a voice that you choose from a premade profile.
Initial uses of this technology are to allow people with good writing skills but bad public speaking skills to bypass the need to record their own speaking. It is also being used to provide more generic narrator style voiceover work rather than hiring a voice actor with a more distinct sound.
There are also dangers in this technology as voice impersonation provides a new avenue for fraud.
Can I video call with an AI?
Yes, it is possible to use AI when making a video call. AI technology can be used to replace video and audio during live video calls and allow for impersonation.
This does have a business benefit as it allows someone to have a default appearance and sound regardless of their current state e.g. a news presenter who is sick still being able to present as they normally would. It will also allow for AI virtual agents and customer service teams to connect with customers on a new level as video interactions are seen as more personal.
However, much like voice replication there are also large potential uses of this technology for fraud. It is easy to imagine a malicious actor who has gained access to an account on a company network calling other people and impersonating the person whose account they have hacked into, and then using that to further their hacking attempts.
How to record a phone call with AI?
To record a phone call with AI, you will need to install or use an application that uses AI to record phone calls. Phone call recording is currently not built into the majority of phone calling apps/smartphones. This means that anyone wishing to record their phone calls with AI will need to install a specific application to do this.
Alternatively, if you are using a collaboration and/or video calling software like Zoom or Microsoft Teams, you will likely find they offer AI call recording and transcription services built in.
AI in contact centre
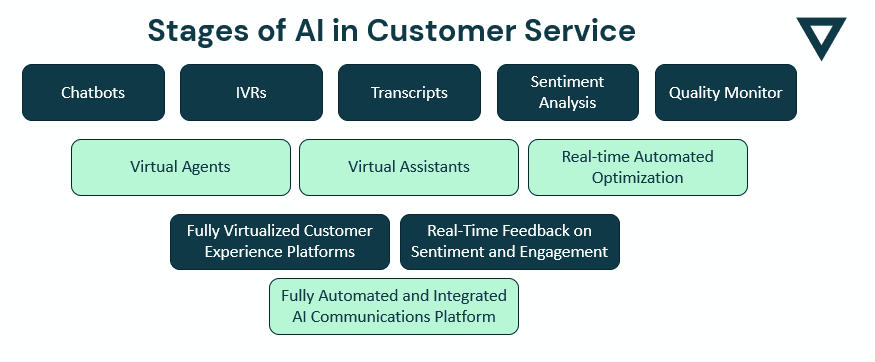
How is AI used in Contact centres?
The main uses for AI in contact centres are the personalisation of the customer experience, and virtual contact centre agents.
AI will be used to personalise the customer journey. This will take the form of either providing a customer service agent with detailed data and conclusions about customers as they interact with the company, or by allowing for the creation of personalised customer journeys for each customer on a large scale.
Simpler AIs will be used to handle frequently asked questions and deal with automated tasks e.g., changing your address. More complex AI will also enable the use of virtual contact centre agents. These agents will be capable of interacting with customers across multiple channels, and making those interactions feel natural and sympathetic.
How is AI used in call centres?
The main use of AI in call centres is to parse through large amounts of call logs and conversation data to provide both insights on customers and training/quality management information about employees.
Rather than having a manager review call logs, or manually search through customer files, AI can instead parse through all of this data and provide valuable insights on customers and their sentiment towards the company.
This approach can also be used to provide feedback to employees about the quality of their interactions, including suggesting areas they can improve. By analysing how customers respond to their statements, employees can be taught to have better customer interactions.
Can AI Replace Call Centre?
AI will never fully replace a call centre. Although chatbots and virtual agents will become popular tools to assist in customer experience, there will always be cases where a customer needs or demands to speak to a real call centre worker.
What is the Future of AI in Contact Centres?
There is no area of contact centre that will remain untouched by AI. Although some companies with simple contact centre needs might not demand AI, it is likely that the solutions they buy will have AI functions included by the provider that optimise the operations on the backend even if the main product is not AI-enabled.
What is Contact Centre as a Service (CCaaS) Software?
Contact Centre as a Service (CCaaS) is a solution that manages inbound customer contact requests and directs them to a call centre agent.
Recently, it is more common for CCaaS solutions to include a group of other options beyond just directing a customer to a call centre agent. These solutions are called Omnichannel solutions because they enable customer contact to span multiple channels. A customer might engage via text/SMS/Chatbot/Phone/Email and all of these systems will be handled by the same solution.
How will AI affect CCaaS?
AI will automate many different types of customer interactions, freeing up employees to handle the more complex interactions.
It will also help to tailor the CCaaS experience to each customer and provide a more tailored service.
What are the main risks of AI in contact centre?
Hallucinations are the main risk of implementing AI technology in the contact centre.
In the context of AI, a hallucination is when the AI does an activity or behaviour that doesn’t match the desired outcome. This can be created for multiple reasons: either the AI operation is wrong, or the data input is wrong. Often these errors are caused by companies either deploying the wrong technology or badly training employees on the use of the technology. The result is customers not getting the positive outcomes they need from interactions and feeling unsatisfied by their experiences.
Hallucinations could drastically affect a customer interaction, especially if a virtual agent means that the customer is only receiving an automated interaction. For this reason, it must always be possible for a customer to reach a human employee regardless of the complexity of the AI solution to ensure they can reach a positive outcome.
What are some examples of AI in CCaaS?
In August 2023, Dialpad announced ‘DialpadGPT’, a large language model (LLM) integration of ChatGPT into the Dialpad ecosystem.
DialpadGPT was built over five years and uses generative AI trained on 5 billion minutes of proprietary conversational data.
The goal of this solution is to automate tasks and improve customer service, sales, and recruiting experiences for businesses.
AI in Customer Service + Support
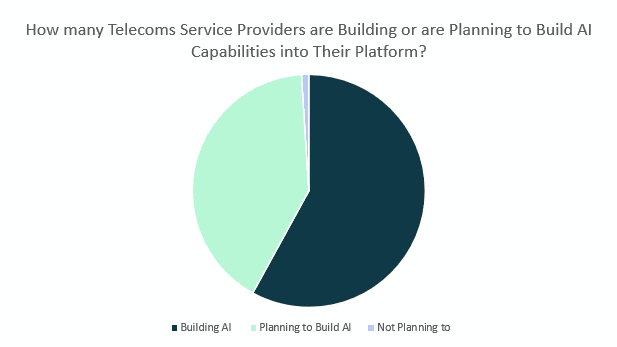
How is AI used in Customer Service?
AI is used to enable more efficient and personalised customer journeys in customer services.
Companies gather large amounts of data on their customers into large data lakes. AI can parse this information and provide summaries of information on each customer, such as their sentiment towards the company, details of previous interactions, likelihood to buy additional services, etc.
This data can be used to automatically create tailored systems that personalise themselves to each customer’s need across every customer service channel.
A chatbot at a telecoms company, for example, could already know that I was having issues with call quality on multiple recent calls, and use that data to understand that I would be more frustrated with the service. It could then offer me tailored discounts or free addons to improve my service quality.
How can AI help customer service?
AI can help customer service by making it much more tailored to the individual. AI can ensure that the maximum amount of data possible about any customer for any interaction is presented to the customer experience solution.
It can also ensure that customer service workers are well-trained, and each have individual feedback and training plans to ensure they provide a good customer experience.
How does AI help customer support?
AI can assist customer support by helping to quickly diagnose and resolve customer support issues.
AI can use its intricate knowledge of both the customer and the services to suggest rapid resolutions to customer issues. AI can even resolve some of these issues for the customer before they become an issue that gets referred to support, which will reduce the overall customer support burden.
An example of this can be seen in the networking industry, where AI can diagnose the most common issues that happen on the network and self-correct them. This means that an issue which would have previously required a customer support ticket no longer needs direct intervention.
What is the future of AI in customer service?
The future of AI in customer service is the gradual replacement of routine customer service tasks with virtual agents.
Not all customer service functions will be replaced with AI, but it will remove a large amount of admin and regular tasks from the workload of customer service staff.
AI in Customer Engagement
How is AI used for Customer Engagement?
The main role of AI in customer engagement is in generating personalised interactions and making customers feel more understood.
One example is the use of generative text abilities to allow the creation of personalised engagement campaigns. Customers respond better to outreach (e.g. emails, text messages) that are tailored to them. These are currently cumbersome to generate, and often companies just target broad demographics (e.g. gender, age) or base it on single data points (e.g. recent purchases), or just change the customer’s name.
However, generative AI allows for the mass creation of tailored emails that will make customers feel much more engaged and more likely to respond to outreach.
What is the role of AI in customer satisfaction?
The primary use for AI in customer satisfaction is the generation of detailed customer insights during interactions.
As loyalty and customer membership schemes have grown, customers have grown less tolerant of company interactions and messaging that does not already know their preferences. Companies are demanding more information from their customers, and customers expect that knowledge to be used.
Customers get even more frustrated if after they have given all this data to a company, that company still doesn’t tailor offers to them, or targets them with incorrect information.
AI bridges this gap by being able to analyse massive data lakes of customer information, both for individual information about a specific customer, but also to predict trends and identify similar customers.
A strong example comes from the insurance industry. A customer making a claim is not just a nameless entity – they have a public history online, a private history with the company, and their case has similarities with other cases that indicate whether they will be paid or rejected.
All this information combined with an AI engine can give a tailored service that pays or contests claims much faster. This leads to higher rates of customer satisfaction.
How does AI impact on customer relationship?
Properly managed AI can have a very positive impact on customer relationships by creating more meaningful and more helpful interactions.
However, there are also risks if AI use is not managed carefully. Customers are still wary of AI and newer technologies, with systems that seem to know ‘too much’ or bots that say things perceived as strange will make customers reject these new systems.
AI and Virtual Agents
What is an example of a virtual agent?
A virtual agent is an intelligent software capable of responding to customer queries automatically.
Originally virtual agents only functioned to answer common FAQ questions over chat and email, but with the advent of generative AI these solutions are getting more complex.
Not only are virtual agents beginning to handle more complex inquiries, but they are also expanding to more channels allowing them to handle more levels of enquiries.
Is a virtual agent real?
This is a common question asked by customers who are worried about interacting with a virtual assistant. They are worried that a virtual agent will lack sympathy and understanding and will therefore not help them get to a positive outcome.
Companies deploying virtual agents need to be aware of this risk of disconnect, and the risk that some customers may just spam nonsense into the system until they are connected to a virtual agent.
Steps need to be taken to make sure a virtual agent responds in a way that feels natural and responsive. Customers that receive a helpful response will be less likely to question whether they are interacting with a real person.
Is a virtual agent the same as a chatbot?
A chatbot can often be a component of a virtual agent platform, as chat is one of the ways that virtual agents communicate.
However, virtual agents are growing in complexity and becoming capable of handling more channels beyond just chatbots, including voice and email.
What are examples of intelligent virtual agents?
Intelligent virtual agents are a more advanced form of virtual agent that is more capable of delivering a conversational and engaging experience across many voice and digital channels.
An example of this can be seen from Five9. They offer the promise that their customers can automate routine and repetitive tasks which allows customers to free up live agents to focus on high value work. The goal of their technology is to use AI to understand what customers want and to provide this, without the intervention of a human agent.
Conclusion
The world of AI in CCaaS is ever changing and constantly growing. Companies selling CCaaS solutions are looking for ways to improve the services they sell to their customers. The goal for them is to enable cost reductions, and to improve efficiency and quality.
They are doing this by harnessing more intelligent AI systems to provide more detailed customer insights and tailored interactions for customers when they are interacting with human agents, and by using other AI systems to automate as many types of interactions with customers as possible.
The end goal is to have a system where all straightforward interactions with customers are handled automatically, which frees up human support resources to dedicate more time towards difficult and complex cases.